Add products by adding codes
A Guide to Modern Portable Memory

In the digital era, data storage has become an integral part of our everyday lives. From portable pendrives, through traditional hard drives (HDD), to modern M.2 drives - the variety of available solutions allows you to adapt the memory to the individual needs of users.
E-SATA connector
E-SATA is an external SATA connector that allows data transfer speeds higher than USB 2.0 but lower than USB 3.0. This is a hybrid connector that can share a port with USB. Its main function is to quickly transfer data between your computer and external storage devices, offering the same speed as internal hard drives.
S-ATA connector
S-ATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) is a serial data bus used to communicate between a computer and storage devices such as HDDs, SSDs, and DVD drives. This is a standard connector used in computers to connect internal hard drives and other storage devices.
PATA vs SATA comparison
SATA is superior to PATA in terms of speed, is hot-pluggable, and has a smaller connector. In contrast, PATA, also known as IDE, is now outdated, offers lower speeds and has limited availability of new accessories.
| PATA | SATA | |
|---|---|---|
| Enlargement | Parallel ATA | Serial ATA |
| Status | Obsolete | In use |
| Hot swapping (hot plugging) | NO | Not |
| External interface | NO | Not |
| Max. cable length | 0.45m | 1m |
| Capacity | 16-133MB/s | 150-600MB/s |
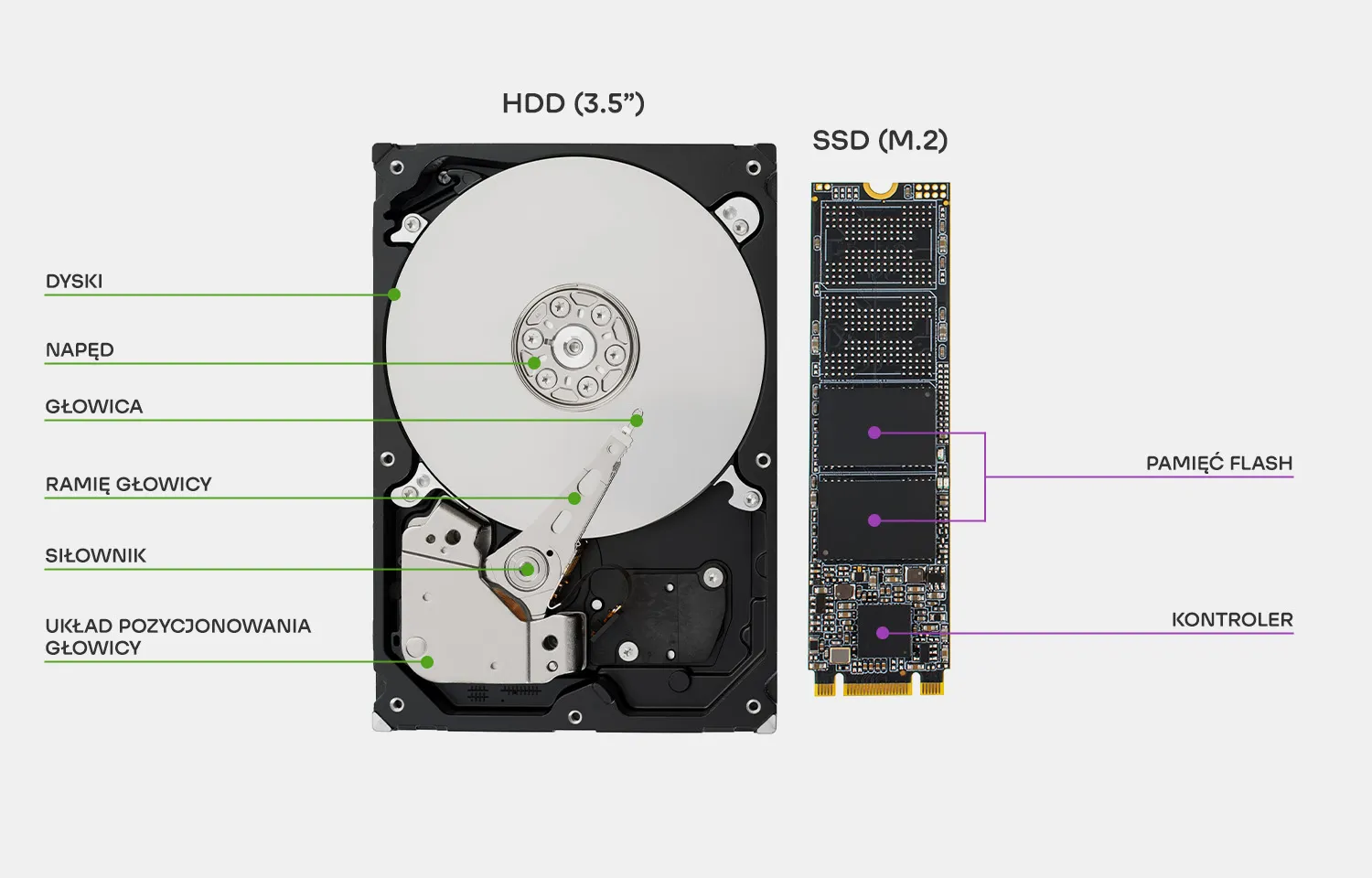
HDD vs SSD - Construction comparison
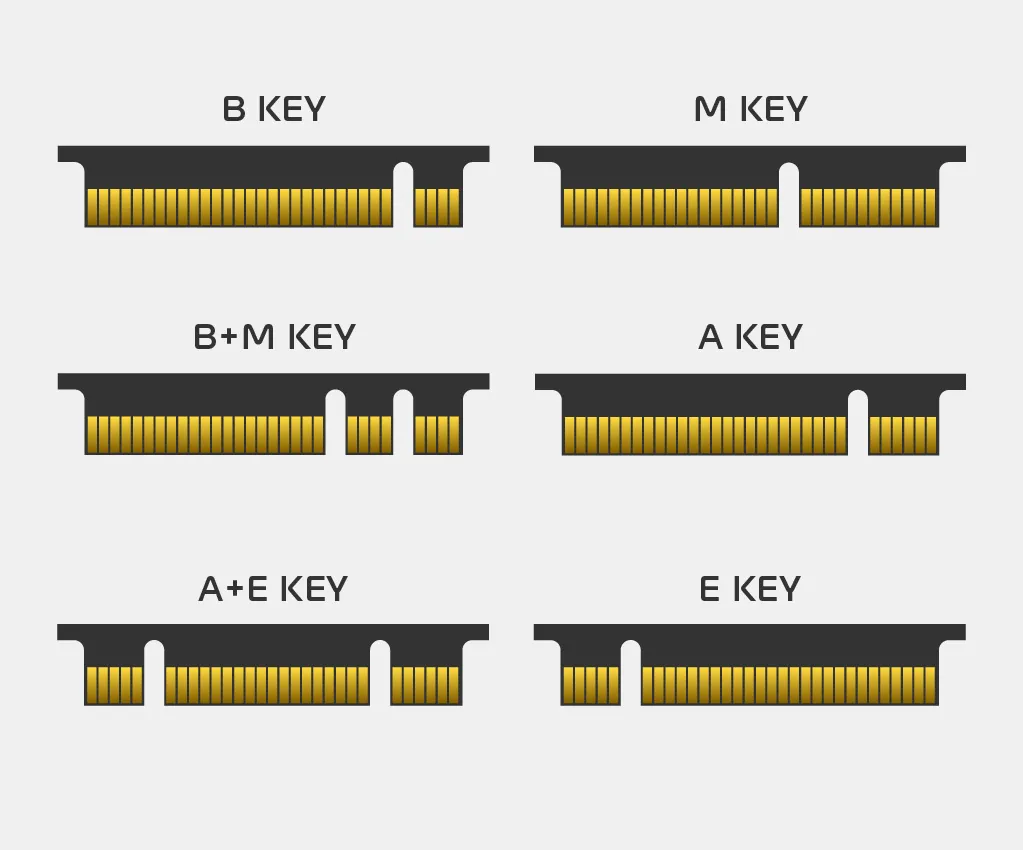
M.2 drive - Characteristics and applications
There are three basic keys in M.2 drives used in current computers/laptops: M, B, M&B. M and M+B keys are compatible.
Additionally, there are A, E and A+E keys.
| Key | Pin location | Interface | App |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 8-15 | 2x PCIe x1, USB2.0, I2C, DP x4 | wireless connectivity Wi-Fi, BT, NFC |
| B | 12-19 | 1x PCIe x2, USB3.0, SATA, HSIC, SSIC, Audio, UIM, I2C | mobile phones & GNSS or SSD |
| C | 16-23 | For future use | |
| D | 20-27 | For future use | |
| E | 24-31 | 2x PCIe x1, USB2.0, I2C, SDIO, UART, PCM | Wi-Fi, BT, NFC, GNSS i/tracking |
| F | 28-35 | For future use | |
| G | 39-46 | Devices not compatible with the M.2 standard | |
| H | 43-50 | For future use | |
| J | 47-54 | For future use | |
| K | 51-58 | For future use | |
| L | 55-62 | For future use | |
| M | 59-66 | PCIe x4, SATA | SSD, AI Accelerator |
Pendrive / Trans Flash / USB Flash Drive
A pendrive is a portable data storage device that uses flash memory and an integrated USB interface. A typical pendrive is small, light (usually less than 30g) and rewritable. Since their introduction to the market in late 2000, the capacity of flash drives has increased from 8 GB to even 1 TB, and from 2023 models with a capacity of 2 TB are available. Some of them can withstand up to 100,000 write/erase cycles, depending on the type of memory used, and are rated to last from 10 to 100 years under normal conditions of use.
External Drives
External hard drives are storage devices that connect to your computer using a USB cable or wirelessly. They are mainly used for media storage, backups, and as extra storage when your computer's internal drive is full. Compared to flash drives, external hard drives offer greater capacity, making them ideal for storing large amounts of data or as network drives for file sharing.
PCIe version vs. slot length on the motherboard - speed comparison
| Slot length | PCIe 1.0 (2003) | PCIe 2.0 (2007) | PCIe 3.0 (2010) | PCIe 4.0 (2017) | PCIe 5.0 (2019) | PCIe 6.0 (2021) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x1 | 0.25 GB/s | 0.5 GB/s | ~1 GB/s | ~2 GB/s | ~4 GB/s | ~8 GB/s |
| x2 | 0.5 GB/s | 1 GB/s | ~2 GB/s | ~4 GB/s | ~8 GB/s | ~16 GB/s |
| x4 | 1 GB/s | 2 GB/s | ~4 GB/s | ~8 GB/s | ~16 GB/s | ~32 GB/s |
| x8 | 2 GB/s | 4 GB/s | ~8 GB/s | ~16 GB/s | ~32 GB/s | ~64 GB/s |
| x16 | 4 GB/s | 8 GB/s | ~16 GB/s | ~32 GB/s | ~64 GB/s | ~128 GB/s |

